Mnist分类任务:
网络基本构建与训练方法,常用函数解析
torch.nn.functional模块
nn.Module模块
读取Mnist数据集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| from pathlib import Path
import requests
DATA_PATH = Path("data")
PATH = DATA_PATH / "mnist"
PATH.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
URL = "http://deeplearning.net/data/mnist/"
FILENAME = "mnist.pkl.gz"
if not (PATH / FILENAME).exists():
content = requests.get(URL + FILENAME).content
(PATH / FILENAME).open("wb").write(content)
|
1
2
3
4
5
| import pickle
import gzip
with gzip.open((PATH / FILENAME).as_posix(), "rb") as f:
((x_train, y_train), (x_valid, y_valid), _) = pickle.load(f, encoding="latin-1")
|
784是mnist数据集每个样本的像素点个数
1
2
3
4
5
| from matplotlib import pyplot
import numpy as np
pyplot.imshow(x_train[0].reshape((28, 28)), cmap="gray")
print(x_train.shape)
|
(50000, 784)
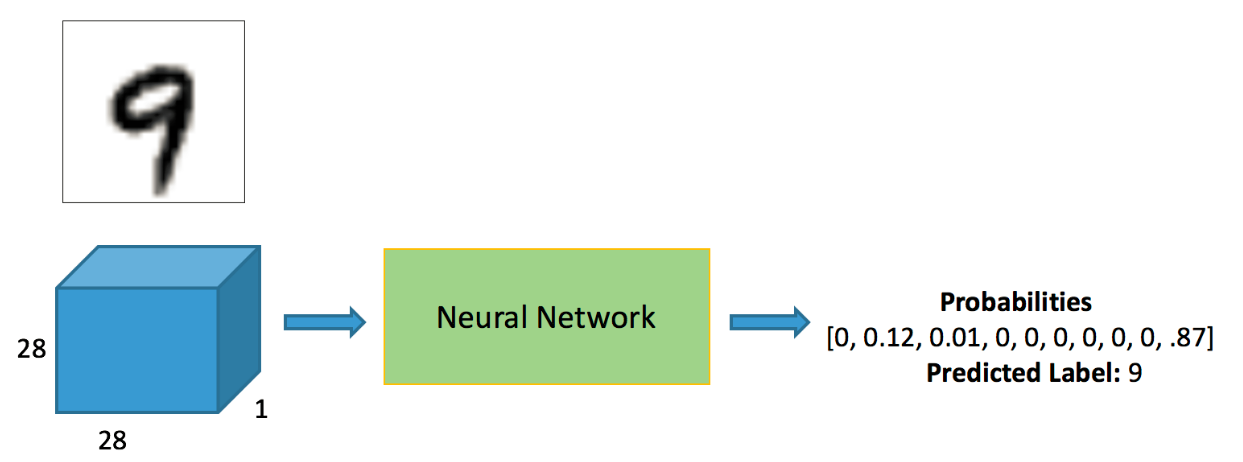
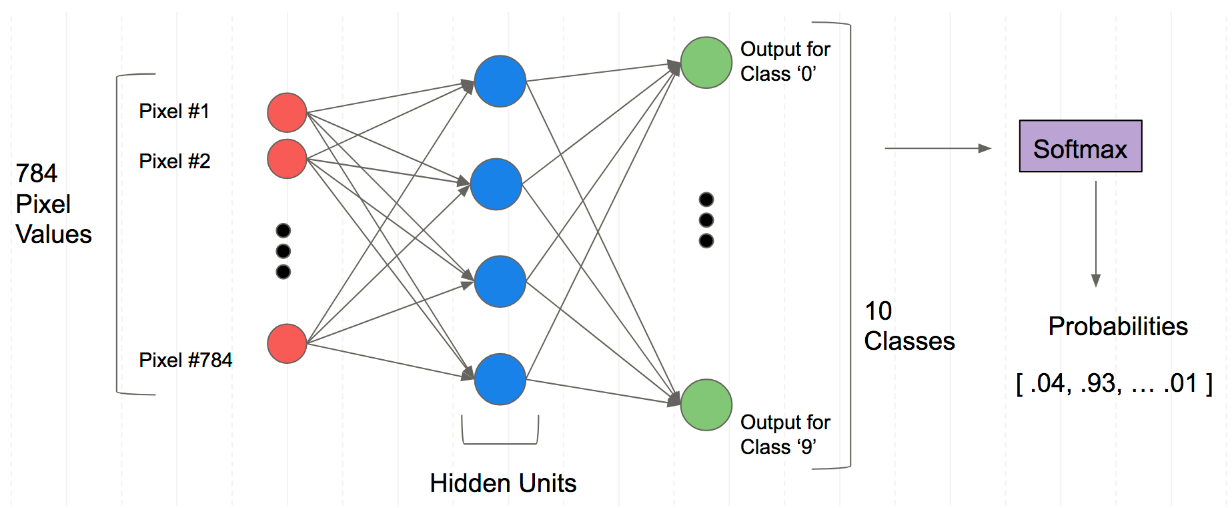
注意数据需转换成tensor才能参与后续建模训练
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import torch
x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid = map(
torch.tensor, (x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid)
)
n, c = x_train.shape
x_train, x_train.shape, y_train.min(), y_train.max()
print(x_train, y_train)
print(x_train.shape)
print(y_train.min(), y_train.max())
|
tensor([[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]]) tensor([5, 0, 4, ..., 8, 4, 8])
torch.Size([50000, 784])
tensor(0) tensor(9)
torch.nn.functional 很多层和函数在这里都会见到
torch.nn.functional中有很多功能,后续会常用的。那什么时候使用nn.Module,什么时候使用nn.functional呢?一般情况下,如果模型有可学习的参数,最好用nn.Module,其他情况nn.functional相对更简单一些
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import torch.nn.functional as F
loss_func = F.cross_entropy
def model(xb):
return xb.mm(weights) + bias
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| bs = 64
xb = x_train[0:bs]
yb = y_train[0:bs]
weights = torch.randn([784, 10], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)
bs = 64
bias = torch.zeros(10, requires_grad=True)
print(loss_func(model(xb), yb))
|
tensor(10.7988, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward>)
创建一个model来更简化代码
- 必须继承nn.Module且在其构造函数中需调用nn.Module的构造函数
- 无需写反向传播函数,nn.Module能够利用autograd自动实现反向传播
- Module中的可学习参数可以通过named_parameters()或者parameters()返回迭代器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| from torch import nn
class Mnist_NN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.hidden1 = nn.Linear(784, 128)
self.hidden2 = nn.Linear(128, 256)
self.out = nn.Linear(256, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hidden1(x))
x = F.relu(self.hidden2(x))
x = self.out(x)
return x
|
1
2
3
| net = Mnist_NN()
print(net)
|
Mnist_NN(
(hidden1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=128, bias=True)
(hidden2): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=256, bias=True)
(out): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
可以打印我们定义好名字里的权重和偏置项
1
2
| for name, parameter in net.named_parameters():
print(name, parameter,parameter.size())
|
hidden1.weight Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.0018, 0.0218, 0.0036, ..., -0.0286, -0.0166, 0.0089],
[-0.0349, 0.0268, 0.0328, ..., 0.0263, 0.0200, -0.0137],
[ 0.0061, 0.0060, -0.0351, ..., 0.0130, -0.0085, 0.0073],
...,
[-0.0231, 0.0195, -0.0205, ..., -0.0207, -0.0103, -0.0223],
[-0.0299, 0.0305, 0.0098, ..., 0.0184, -0.0247, -0.0207],
[-0.0306, -0.0252, -0.0341, ..., 0.0136, -0.0285, 0.0057]],
requires_grad=True) torch.Size([128, 784])
hidden1.bias Parameter containing:
tensor([ 0.0072, -0.0269, -0.0320, -0.0162, 0.0102, 0.0189, -0.0118, -0.0063,
-0.0277, 0.0349, 0.0267, -0.0035, 0.0127, -0.0152, -0.0070, 0.0228,
-0.0029, 0.0049, 0.0072, 0.0002, -0.0356, 0.0097, -0.0003, -0.0223,
-0.0028, -0.0120, -0.0060, -0.0063, 0.0237, 0.0142, 0.0044, -0.0005,
0.0349, -0.0132, 0.0138, -0.0295, -0.0299, 0.0074, 0.0231, 0.0292,
-0.0178, 0.0046, 0.0043, -0.0195, 0.0175, -0.0069, 0.0228, 0.0169,
0.0339, 0.0245, -0.0326, -0.0260, -0.0029, 0.0028, 0.0322, -0.0209,
-0.0287, 0.0195, 0.0188, 0.0261, 0.0148, -0.0195, -0.0094, -0.0294,
-0.0209, -0.0142, 0.0131, 0.0273, 0.0017, 0.0219, 0.0187, 0.0161,
0.0203, 0.0332, 0.0225, 0.0154, 0.0169, -0.0346, -0.0114, 0.0277,
0.0292, -0.0164, 0.0001, -0.0299, -0.0076, -0.0128, -0.0076, -0.0080,
-0.0209, -0.0194, -0.0143, 0.0292, -0.0316, -0.0188, -0.0052, 0.0013,
-0.0247, 0.0352, -0.0253, -0.0306, 0.0035, -0.0253, 0.0167, -0.0260,
-0.0179, -0.0342, 0.0033, -0.0287, -0.0272, 0.0238, 0.0323, 0.0108,
0.0097, 0.0219, 0.0111, 0.0208, -0.0279, 0.0324, -0.0325, -0.0166,
-0.0010, -0.0007, 0.0298, 0.0329, 0.0012, -0.0073, -0.0010, 0.0057],
requires_grad=True) torch.Size([128])
hidden2.weight Parameter containing:
tensor([[-0.0383, -0.0649, 0.0665, ..., -0.0312, 0.0394, -0.0801],
[-0.0189, -0.0342, 0.0431, ..., -0.0321, 0.0072, 0.0367],
[ 0.0289, 0.0780, 0.0496, ..., 0.0018, -0.0604, -0.0156],
...,
[-0.0360, 0.0394, -0.0615, ..., 0.0233, -0.0536, -0.0266],
[ 0.0416, 0.0082, -0.0345, ..., 0.0808, -0.0308, -0.0403],
[-0.0477, 0.0136, -0.0408, ..., 0.0180, -0.0316, -0.0782]],
requires_grad=True) torch.Size([256, 128])
hidden2.bias Parameter containing:
tensor([-0.0694, -0.0363, -0.0178, 0.0206, -0.0875, -0.0876, -0.0369, -0.0386,
0.0642, -0.0738, -0.0017, -0.0243, -0.0054, 0.0757, -0.0254, 0.0050,
0.0519, -0.0695, 0.0318, -0.0042, -0.0189, -0.0263, -0.0627, -0.0691,
0.0713, -0.0696, -0.0672, 0.0297, 0.0102, 0.0040, 0.0830, 0.0214,
0.0714, 0.0327, -0.0582, -0.0354, 0.0621, 0.0475, 0.0490, 0.0331,
-0.0111, -0.0469, -0.0695, -0.0062, -0.0432, -0.0132, -0.0856, -0.0219,
-0.0185, -0.0517, 0.0017, -0.0788, -0.0403, 0.0039, 0.0544, -0.0496,
0.0588, -0.0068, 0.0496, 0.0588, -0.0100, 0.0731, 0.0071, -0.0155,
-0.0872, -0.0504, 0.0499, 0.0628, -0.0057, 0.0530, -0.0518, -0.0049,
0.0767, 0.0743, 0.0748, -0.0438, 0.0235, -0.0809, 0.0140, -0.0374,
0.0615, -0.0177, 0.0061, -0.0013, -0.0138, -0.0750, -0.0550, 0.0732,
0.0050, 0.0778, 0.0415, 0.0487, 0.0522, 0.0867, -0.0255, -0.0264,
0.0829, 0.0599, 0.0194, 0.0831, -0.0562, 0.0487, -0.0411, 0.0237,
0.0347, -0.0194, -0.0560, -0.0562, -0.0076, 0.0459, -0.0477, 0.0345,
-0.0575, -0.0005, 0.0174, 0.0855, -0.0257, -0.0279, -0.0348, -0.0114,
-0.0823, -0.0075, -0.0524, 0.0331, 0.0387, -0.0575, 0.0068, -0.0590,
-0.0101, -0.0880, -0.0375, 0.0033, -0.0172, -0.0641, -0.0797, 0.0407,
0.0741, -0.0041, -0.0608, 0.0672, -0.0464, -0.0716, -0.0191, -0.0645,
0.0397, 0.0013, 0.0063, 0.0370, 0.0475, -0.0535, 0.0721, -0.0431,
0.0053, -0.0568, -0.0228, -0.0260, -0.0784, -0.0148, 0.0229, -0.0095,
-0.0040, 0.0025, 0.0781, 0.0140, -0.0561, 0.0384, -0.0011, -0.0366,
0.0345, 0.0015, 0.0294, -0.0734, -0.0852, -0.0015, -0.0747, -0.0100,
0.0801, -0.0739, 0.0611, 0.0536, 0.0298, -0.0097, 0.0017, -0.0398,
0.0076, -0.0759, -0.0293, 0.0344, -0.0463, -0.0270, 0.0447, 0.0814,
-0.0193, -0.0559, 0.0160, 0.0216, -0.0346, 0.0316, 0.0881, -0.0652,
-0.0169, 0.0117, -0.0107, -0.0754, -0.0231, -0.0291, 0.0210, 0.0427,
0.0418, 0.0040, 0.0762, 0.0645, -0.0368, -0.0229, -0.0569, -0.0881,
-0.0660, 0.0297, 0.0433, -0.0777, 0.0212, -0.0601, 0.0795, -0.0511,
-0.0634, 0.0720, 0.0016, 0.0693, -0.0547, -0.0652, -0.0480, 0.0759,
0.0194, -0.0328, -0.0211, -0.0025, -0.0055, -0.0157, 0.0817, 0.0030,
0.0310, -0.0735, 0.0160, -0.0368, 0.0528, -0.0675, -0.0083, -0.0427,
-0.0872, 0.0699, 0.0795, -0.0738, -0.0639, 0.0350, 0.0114, 0.0303],
requires_grad=True) torch.Size([256])
out.weight Parameter containing:
tensor([[ 0.0232, -0.0571, 0.0439, ..., -0.0417, -0.0237, 0.0183],
[ 0.0210, 0.0607, 0.0277, ..., -0.0015, 0.0571, 0.0502],
[ 0.0297, -0.0393, 0.0616, ..., 0.0131, -0.0163, -0.0239],
...,
[ 0.0416, 0.0309, -0.0441, ..., -0.0493, 0.0284, -0.0230],
[ 0.0404, -0.0564, 0.0442, ..., -0.0271, -0.0526, -0.0554],
[-0.0404, -0.0049, -0.0256, ..., -0.0262, -0.0130, 0.0057]],
requires_grad=True) torch.Size([10, 256])
out.bias Parameter containing:
tensor([-0.0536, 0.0007, 0.0227, -0.0072, -0.0168, -0.0125, -0.0207, -0.0558,
0.0579, -0.0439], requires_grad=True) torch.Size([10])
使用TensorDataset和DataLoader来简化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_ds = TensorDataset(x_train, y_train)
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=bs, shuffle=True)
valid_ds = TensorDataset(x_valid, y_valid)
valid_dl = DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=bs * 2)
|
1
2
3
4
5
| def get_data(train_ds, valid_ds, bs):
return (
DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=bs, shuffle=True),
DataLoader(valid_ds, batch_size=bs * 2),
)
|
- 一般在训练模型时加上model.train(),这样会正常使用Batch Normalization和 Dropout
- 测试的时候一般选择model.eval(),这样就不会使用Batch Normalization和 Dropout
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import numpy as np
def fit(steps, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, valid_dl):
for step in range(steps):
model.train()
for xb, yb in train_dl:
loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb, opt)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
losses, nums = zip(
*[loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb) for xb, yb in valid_dl]
)
val_loss = np.sum(np.multiply(losses, nums)) / np.sum(nums)
print('当前step:'+str(step), '验证集损失:'+str(val_loss))
|
1
2
3
4
| from torch import optim
def get_model():
model = Mnist_NN()
return model, optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| def loss_batch(model, loss_func, xb, yb, opt=None):
loss = loss_func(model(xb), yb)
if opt is not None:
loss.backward()
opt.step()
opt.zero_grad()
return loss.item(), len(xb)
|
三行搞定!
1
2
3
| train_dl, valid_dl = get_data(train_ds, valid_ds, bs)
model, opt = get_model()
fit(25, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, valid_dl)
|
当前step:0 验证集损失:2.2796445930480957
当前step:1 验证集损失:2.2440698066711424
当前step:2 验证集损失:2.1889826164245605
当前step:3 验证集损失:2.0985311767578123
当前step:4 验证集损失:1.9517273582458496
当前step:5 验证集损失:1.7341805934906005
当前step:6 验证集损失:1.4719875366210937
当前step:7 验证集损失:1.2273896869659424
当前step:8 验证集损失:1.0362271406173706
当前step:9 验证集损失:0.8963696184158325
当前step:10 验证集损失:0.7927186088562012
当前step:11 验证集损失:0.7141492074012756
当前step:12 验证集损失:0.6529350900650024
当前step:13 验证集损失:0.60417300491333
当前step:14 验证集损失:0.5643046331882476
当前step:15 验证集损失:0.5317994566917419
当前step:16 验证集损失:0.5047958114624024
当前step:17 验证集损失:0.4813900615692139
当前step:18 验证集损失:0.4618900228500366
当前step:19 验证集损失:0.4443243554592133
当前step:20 验证集损失:0.4297310716629028
当前step:21 验证集损失:0.416976597738266
当前step:22 验证集损失:0.406348459148407
当前step:23 验证集损失:0.3963301926612854
当前step:24 验证集损失:0.38733808159828187